Genome transcriptional regulation
Topics
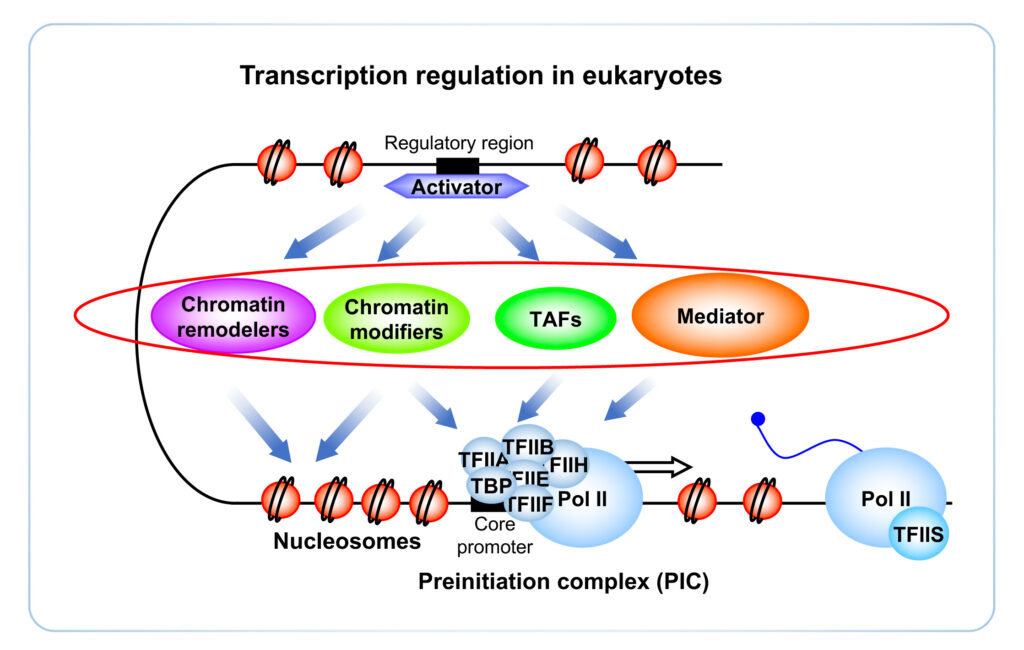
In eukaryotes, transcription is highly regulated and involves many multiprotein complexes. One of these complexes, the Mediator of transcriptional regulation, plays a crucial role in the activation of transcription by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), as it integrates the signals of specific transcription factors and stimulates the recruitment of Pol II (Soutourina, 2018). However, the complexity of Mediator has precluded a detailed understanding of its mechanisms of action, essential for the study of the regulation of gene expression. In humans, mutations that affect Mediator subunits lead to a number of pathologies, including cancers, which underscore the importance of understanding the Mediator function for human health.
We are studying the molecular mechanisms of the Mediator function in transcription activation and, in particular, in preinitiation complex (PIC) formation. Using the power of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as our main model and integrative biology approaches, we have demonstrated the essential links of this complex with components of the transcriptional machinery, such as TFIIH, RNA polymerase II, TFIIS or TFIIB in relation to the promoter architecture that contributed to the understanding of Mediator function (Esnault et al. 2008, Soutourina et al. 2011, Eyboulet et al. 2015, Eychenne et al, 2016).
Using our genomic data, we aim to model the PIC assembly pathways in order to understand the rules that determine the recruitment of the transcriptional machinery in vivo in relation to the promoter architecture, the chromatin organization and the transcription factors involved. Currently, we are also addressing the questions of the conservation of yeast mechanisms to human cells in the chromatin context. We believe that our work will help us to understand how Mediator acts as a coregulatory complex and how its dysfunction could lead to disease.
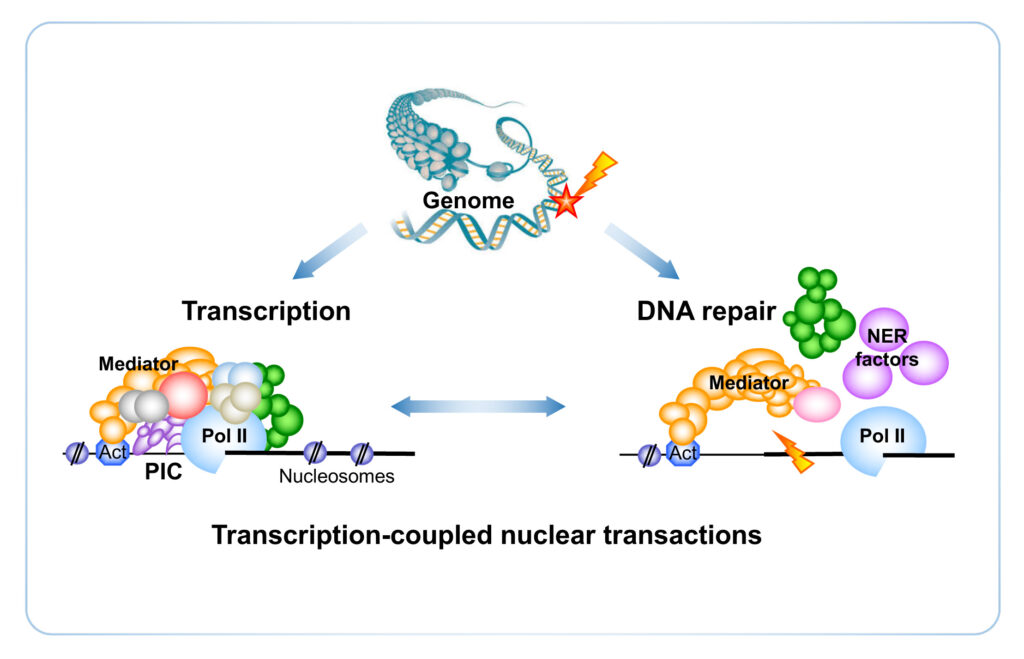
Transcription is coupled with DNA repair, ensuring the continuity of Pol II progression. DNA damage can potentially lead to problems in development, cell growth and survival. Components of transcription or repair machineries can participate in both processes. Nucleotide-excision DNA repair (NER) is a major pathway of DNA repair that removes DNA lesions such as cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD) arising upon UV irradiation. Global genome repair pathway operates on the genome overall and transcription-coupled repair removes DNA lesions that interfere with the progression of Pol II. While the NER reaction and the components required for efficient DNA lesion recognition and repair are fairly well understood in vitro, many questions on the active coupling between transcription and DNA repair remain still unanswered in vivo, notably on the genomic scale.
Recently, we have discovered a novel role of the Mediator complex by connecting transcription and DNA repair via a direct contact with Rad2 endonuclease, the yeast homolog of human XPG protein (Eyboulet et al. 2013, Georges et al. 2019). Mutations in the human XPG gene give rise to a genetic disease, xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) associated with Cockayne syndrome (CS). Our results indicate that Mediator is involved in transcription-coupled repair by facilitating the recruitment of Rad2 to transcribed genes. We propose that in addition to its fundamental co-activator role, Mediator acts in essential nuclear processes beyond transcription (Eyboulet et al. 2013; André, Sipos, Soutourina 2021).
We wish to contribute to the understanding of the complex link between transcription and DNA repair mechanisms in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in human cells and to model the in vivo orchestration of the repair mechanisms coupled with transcription. Transcription influences genetic integrity by also affecting DNA mutagenesis, and mutations in DNA have large-ranging consequences, from driving the evolution process to causing cancers. We thus wish to understand the molecular mechanisms involved in mutagenesis associated with transcription. The coordination of different fundamental processes in vivo in eukaryotes remains a key biological question that is directly related to serious human pathologies.