Structural biochemistry
of bacterial transporters
Our team is interested in elucidating action mechanisms of singles proteins and within multi-molecular complexes including transporters.
Our work allows supplying fundamental basis describing molecular function at atomic level. Our team possesses a strong expertise in structural analysis by crystallography of (i) bacterial, plant, phage and human enzymatic mechanisms, (ii) bacterial transport systems for opines, metals, peptides (iii) bacterial and human proteins interacting with DNA such as DNA repair/modification enzymes, transcriptional factors. For short, we are specialized in the study of protein-protein interactions, protein-DNA and protein-ligand interactions, which are at the center of all the biological processes.
Our general goal is to characterize the molecular role of transporters in bacteria using biochemical, structural and biophysics techniques. During 12 years, the team delved into the study of opine transporters from the plant pathogen Agrobacterium focusing on the soluble part denoted Solute Binding Proteins (SBP) of the ABC transporters, as these SBPs played a crucial role in transport specificity. Opine transporters are involved in host-pathogen relationship, nutrient transport and virulence.
The team is exploring complex machineries, such as metal transporters, involving several soluble and membrane proteins. We are studying the two bacterial iron transport systems denoted Fpv from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Ftr from pathogenic Bordetella, Brucella and Burkholderia bacteria. The aim is to understand how these two transporters work.
Experimental approach
- Production of proteins (cloning, mutagenesis, bacterial culture…)
- Purification of recombinant proteins (Chromatography of affinity, Gel filtration…)
- Enzymatic tests and inhibition measurement (Spectrophotometry)
- Crystallization (standard and Lipidic cubic phase (LCP) methods)
- X-rays crystallography and CryoEM
- Interactions determination (Microcalorimétrie, Fluorescence, DSC)
- Conformational analyses (Circular Dichroism, Ultracentrifugation, light scattering)
- Bioinformatic and molecular modelisation (AutoDock, MD, AlphaFold)
Examples of recent works
A- Iron transport through the bacterial Ftr-system (Steunou et al. 2022), The FEBS Journal 289, 6286-6307 doi: 10.1111/febs.16476)
Iron is essential for the survival of bacteria. Its ferrous form, mainly present in low-oxygen and acidic pH environments, can be imported into bacteria via the specific Ftr-type transport system, such as the FtrABCD system, conserved in many pathogenic bacteria such as Bordetella, Brucella and Burkholderia. A fruitful internal collaboration between microbiologists, spectroscopists and our team has provided new insights, combining in vivo and in vitro approaches, into the regulation of this iron transporter and the role of the periplasmic proteins FtrA and FtrB. The structures of FtrA in the presence or absence of copper and copper-iron enabled the sequential description of the steps involved in binding iron to the protein. They revealed that copper binding in the first metal site of the protein was essential, displacing a histidine and allowing iron to bind in the second metal site, 7 Å away from the copper site. Once bound, FtrA oxidises the ferrous ion to ferric iron through reduction of the copper ion. As for FtrB, we have shown that it binds iron and hypothesise that it plays a chaperone role. Our results enable us to propose a new functional model for the mechanism of ferrous iron import by the FtrABCD iron transporter.
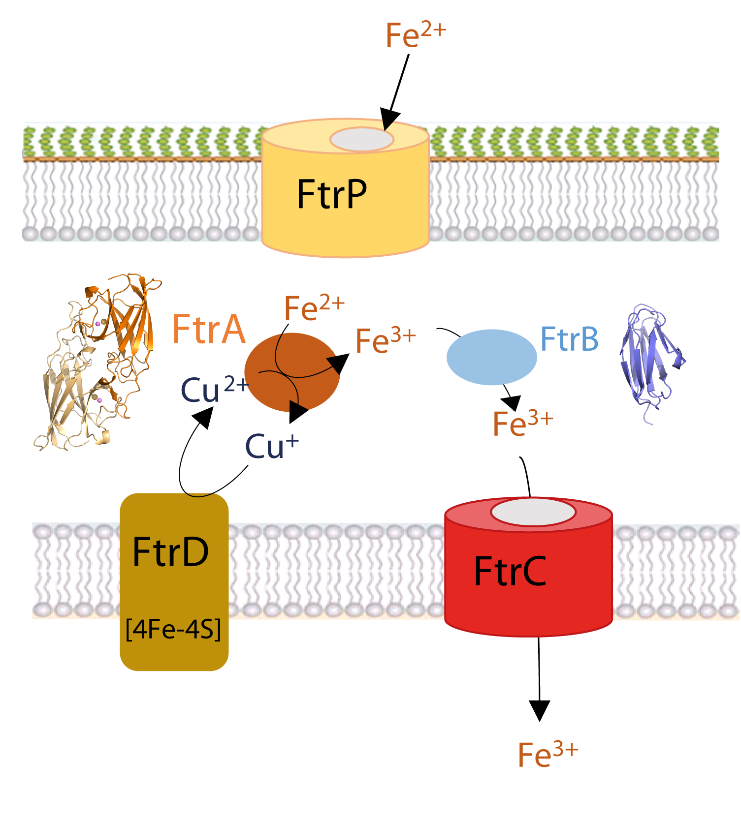
Figure legend: A proposed model for the ferrous iron transporter, FtrAPBCD in R. gelatinosus. The ferrous ion enters the periplasm via the FtrP porin located in the cell outer membrane. It is sequestered by the copper-dependent periplasmic ferrous iron oxidase FtrA. The oxidised iron is then taken up by the chaperone FtrB, which delivers the ferric iron to the permease FtrC for transport into the cytoplasm. The electrons produced by the oxidation of iron by copper in FtrA are recycled by the polyferredoxin FtrD, which acts as an electron sink and resets the ferrous iron import system. The crystal structure of FtrA in the presence of copper and iron and the modelling of the structure of FtrB are shown.
B- Import pathways of the mannityl-opines into the bacterial pathogen A.tumefaciens (Vigouroux et al. 2020, Biochem J. 477, 615-628).
Agrobacterium tumefaciens pathogens use specific compounds namely opines as nutrients in their plant tumor niche. These opines are produced by the host plant cells genetically modified by agrobacteria. They are imported into bacteria via solute-binding proteins (SBPs) in association with ABC transporters. The mannityl-opine family encompasses mannopine, mannopinic acid, agropine and agropinic acid. Combining in vitro and in vivo approaches, our work finalizes the characterization of the mannityl-opines assimilation pathways, highlighting the important role of two dual imports of agropinic and mannopinic acids. Our data shed new light on how the mannityl-opines contribute to the establishment of the ecological niche of agrobacteria from the early to the late stages of tumor development.
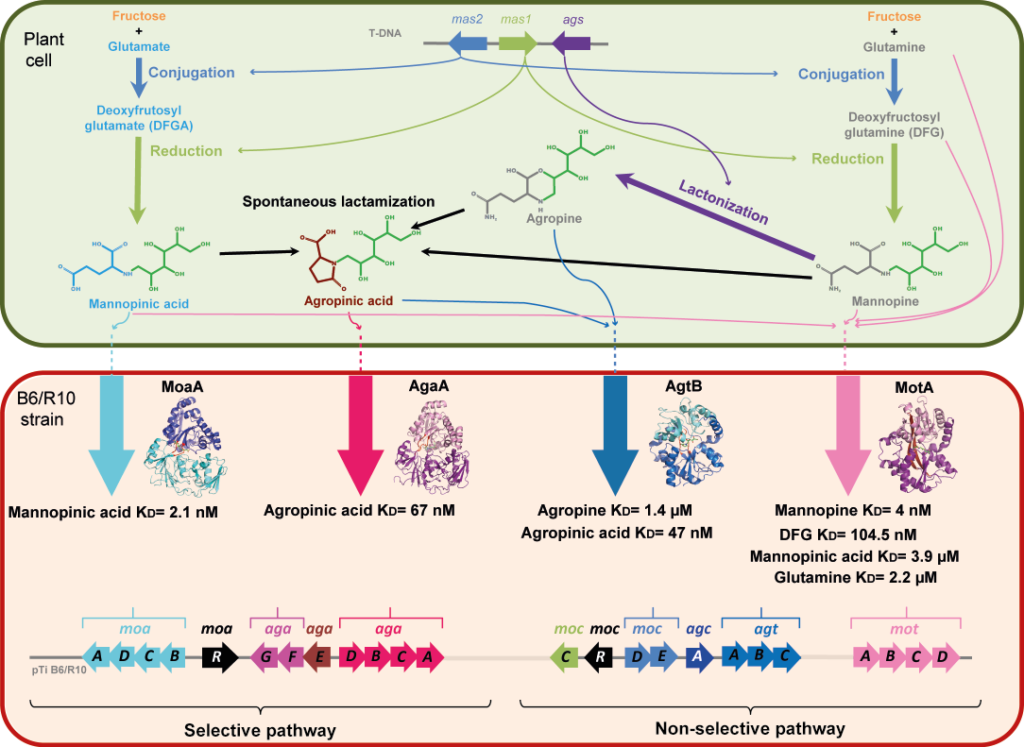
Figure legend: Metabolism of mannityl-opines in transformed plant cells and in A. tumefaciens R10/B6 strains. In modified plant cell, the mas1 and mas2 genes responsible for the biosynthesis of mannopinic acid and mannopine are located on the T-DNA as well as ags gene product, which catalyzes the lactonization of mannopine to agropine. Agropinic acid results from a spontaneous lactamization of the three mannityl-opines: agropine, mannopine and mannopinic acid. In A. tumefaciens B6/R10 strain, two transport pathways for agropinic acid and mannopinic acid co-exist. The (moaADCB) genes (cyan) and the (motABDC) genes (pink) located on the Ti plasmid code for the selective and non-selective transport of mannopinic acid, respectively. The (agaACDB) genes (magenta) and (agtABC) genes (blue) code for the selective and non-selective transport of agropinic acid, respectively. The structure of the four SBPs MoaA-, AgaA-, AgtB- and MotA-mediated transport bound to their preferred mannityl-opine, which are mannopinic acid, agropinic acid, agropine and mannopine, respectively are shown. Affinity values are indicated. The (agaE), (agaFG), (agcA), (mocC) and (mocDE) genes products are involved in mannityl-opines degradation. The (moaR) and (mocR) genes code for a corresponding transcriptional regulator of each genes clusters.
C- The transcriptional repressor Atu1419 from the bacterial pathogen A.tumefaciens (Vigouroux et al, (2021), NAR 49, 529-546 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1181)
A species-specific region, denoted SpG8-1b allowing hydroxycinnamic acids (HCAs) degradation is important for the transition between the two lifestyles (rhizospheric versus pathogenic) of the plant pathogen Agrobacterium fabrum. Indeed, HCAs can be either used as trophic resources and/or as induced-virulence molecules. The SpG8-1b region is regulated by two transcriptional regulators, namely, HcaR (Atu1422) and Atu1419. Our structural study revealed that the tetrameric Atu1419 transcriptional regulator belongs to the VanR group of Pfam PF07729 subfamily of the large GntR superfamily. Until now, GntR regulators were described as dimers. We showed that Atu1419 represses three genes of the HCAs catabolic pathway. We characterized both the effector and DNA binding sites and identified key nucleotides in the target palindrome.
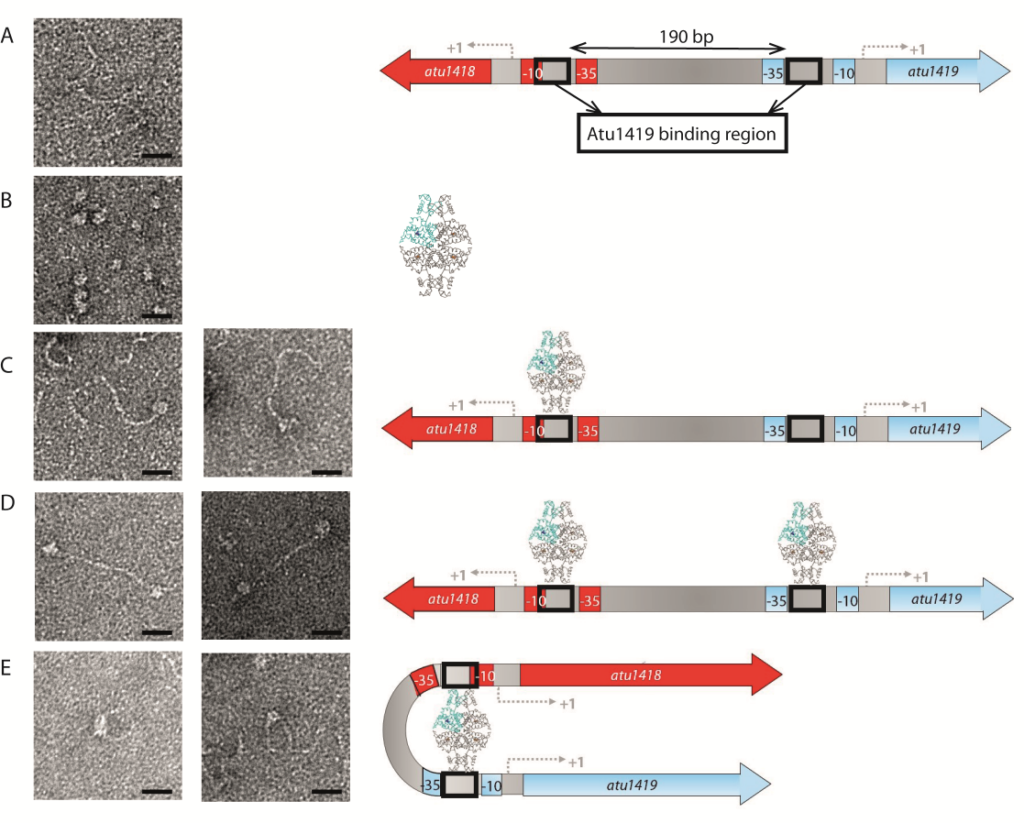
Figure legend: Interactions between Atu1419 repressor and Patu1418-1419 region of 370 bp containing two palindromes separated by 190 bp visualized by electron microscopy on the left, and corresponding models on the right. (A) Image of Patu1418-1419 region, (B) Image of Atu1419 tetramer, (C) Image of one tetramer bound to one palindrome, (D) Image of two tetramers bound each to one palindrome, (E) Image of one tetramer inducing a DNA loop. Scales bars: 20 nm.
team

Group Leader Senior Researcher

Engineer
Engineer
Alumni
Former PhD students
Grégory Deicsics (2017-2020)
Marion Gransagne (2014-2017)
Loïc Marty (2013-2016)
Abbas El-Shaili (2012-2015)
Former CDD
Dorian Lefebvre, CDD EI (10/2020-10/2021)
Emeline Thuleau, L3 pro de Biotechnologies et Bio-industries (10/19-03/20)
Léa Lo Bello, L3 pro de Biotechnologies et Bio-industries (10/18-09/19)
Coralie Carivenc, CDD AI (09/2016-11/2016)
Former students (Licence and Master)
Juliette Grosjean, M1 Plateforme Microbiologie (03/2025-06/2025)
Zoé Gadal, L2 double licence Chimie-Biologie (04/2025-06/2025)
Inès Deso, L2 Chimie (04/2024-06/2024)
Emilie Alves, L2 de Biologie (04/2023-06/2023)
Stelia-Wendy Gassin, L2 de Biologie (04/2023-06/2023)
Laurine Langlois, Double licence Biologie-Chimie (04/2022-06/2022)
Marine Le Berre, Magistère de Biologie (06/19-07/19)
Margot Draveny, L2 de Biologie (04/18-06/18)
Isabelle Dias Da Silva, L2 de Biologie (07/2016-08/2016)
Anaïs Naretto, M2 ingénierie moléculaire (01/2015-06/2015)
Latest publications
Travin, Dmitrii Y., Romain Jouan, Armelle Vigouroux, Satomi Inaba-Inoue, Joy Lachat, Fazal Haq, Tatiana Timchenko, et al. 2023. “Dual-Uptake Mode of the Antibiotic Phazolicin Prevents Resistance Acquisition by Gram-Negative Bacteria.” MBio, February, e0021723. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00217-23.
Bělíček, Jakub, Eva Ľuptáková, David Kopečný, Jan Frömmel, Armelle Vigouroux, Sanja Ćavar Zeljković, Franjo Jagic, et al. 2023. “Biochemical Ans Structural Basis of Polyamine, Lysine and Ornithine Acetylation Catalyzed by Spermine/Spermidine N-Acetyl Transferase in Moss and Maize.” The Plant Journal: For Cell and Molecular Biology, February. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.16148.
Partners
I2BC Facilities

Synchrotron SOLEIL








