Autophagy, Stress and Development
Topics
The family of Atg8/LC3 “ubiquitin-like” proteins play multiple roles in autophagy.
With only one LC3 and one Gabarap homolog, C. elegans is a good paradigm to understand their specific functions. We have shown that they are essential for multiple physiological processes during development, stress and aging and have a synergistic role in several aspects of development. We demonstrated that LGG-1 is essential for the formation of autophagosomes and acts upstream of LGG-2 which interacts directly with the HOPS complex and favors fusion with lysosome, a cellular acidic compartment.
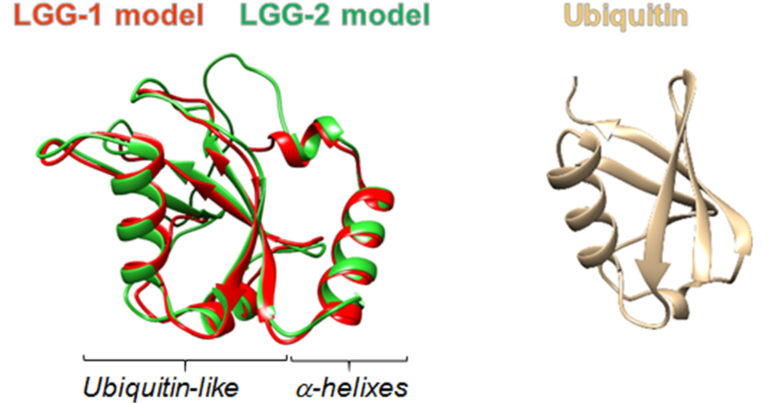
LGG-1/GABARAP lipidation is not required for autophagy and development in Caenorhabditis elegans
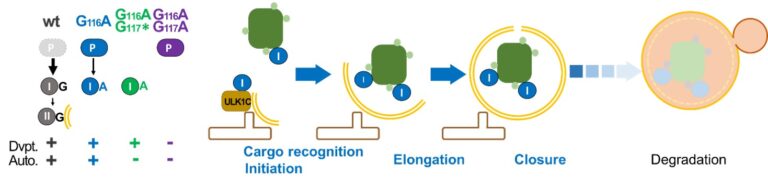
Most of the functions of LC3/GABARAP in macroautophagy/autophagy are considered to depend on their association with the phagophore membrane through a conjugation to a lipid. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we inhibited the conjugation of LGG-1, the single homolog of GABARAP in C. elegans. Mutants that express only cytosolic forms revealed an essential role for the cleaved form of LGG-1 in autophagy but also in an autophagy-independent embryonic function.
We have analyzed the functional links between endosomal maturation and autophagy and reported the first evidence of amphisomes in C. elegans. We also discovered a novel function of ESCRT-II components in the maintenance of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) integrity in muscles.
Leboutet, R., Largeau, C., Müller, L., Prigent, M., Quinet, G., Rodriguez, M. S., Cuif, M. H., Hoppe, T., Culetto, E., Lefebvre, C., & Legouis, R. LGG-1/GABARAP lipidation is not required for autophagy and development in Caenorhabditis elegans. eLife 2023
Leboutet, R., Largeau, C., Culetto, E., Lefebvre, C., Hoppe, T., & Legouis, R. Membrane localization of LGG-1/GABARAP is dispensable for autophagy in C. elegans. Autophagy 2023 19(12), 3254–3255 12, e85748
Jenzer C, Simionato E, LARGEAU C, Scarcelli V, Lefebvre C, Legouis R. Autophagy mediates phosphatidylserine exposure and phagosome degradation during apoptosis through specific functions of GABARAP/LGG-1 and LC3/LGG-2. Autophagy. 2019 Feb;15(2):228-241.
Jenzer C, Legouis R. Multiple functions of autophagy during development. Med Sci (Paris). 2017 Mar;33(3):238-245. Review
Manil-Ségalen M, Lefebvre C, Jenzer C, Trichet M, Boulogne C, Satiat-Jeunemaitre B, Legouis R. The C. elegans LC3 acts downstream of GABARAP to degrade autophagosomes by interacting with the HOPS subunit VPS39. Dev Cell. 2014 Jan 13;28(1):43-55.
Lefebvre C, Largeau C, Michelet X, Fourrage C, Maniere X, Matic I, Legouis R*, Culetto E. The ESCRT-II proteins are involved in shaping the sarcoplasmic reticulum in C. elegans. J Cell Sci. 2016 Apr 1;129(7):1490-9.
Manil-Ségalen M, Culetto E, Legouis R, Lefebvre C. Interactions between endosomal maturation and autophagy: analysis of ESCRT machinery during Caenorhabditis elegans development. Methods Enzymol. 2014;534:93-118.
Djeddi A, Michelet X, Culetto E, Alberti A, Barois N, Legouis R. Induction of autophagy in ESCRT mutants is an adaptive response for cell survival in C. elegans. J Cell Sci. 2012 Feb 1;125(Pt 3):685-94.
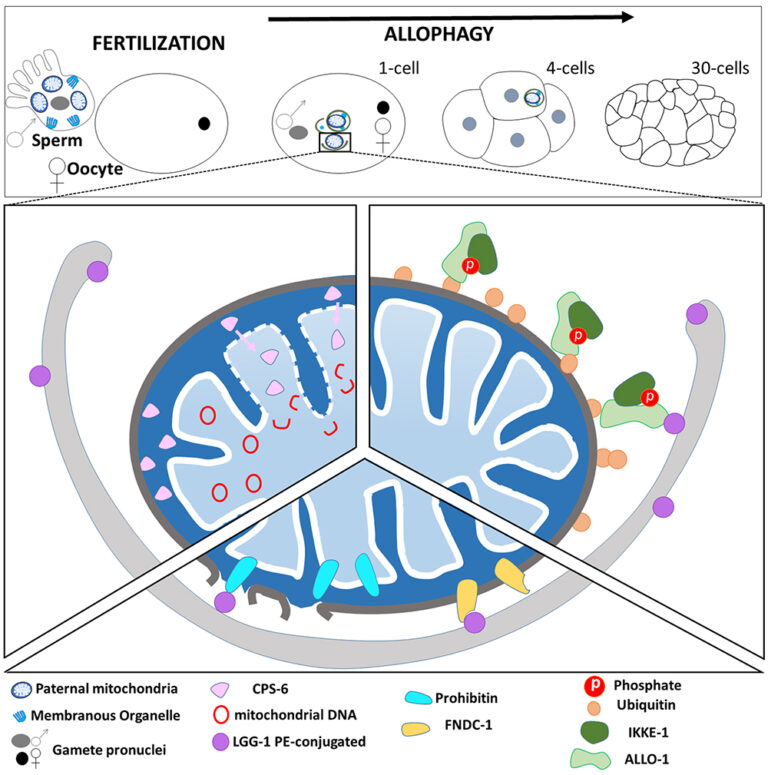
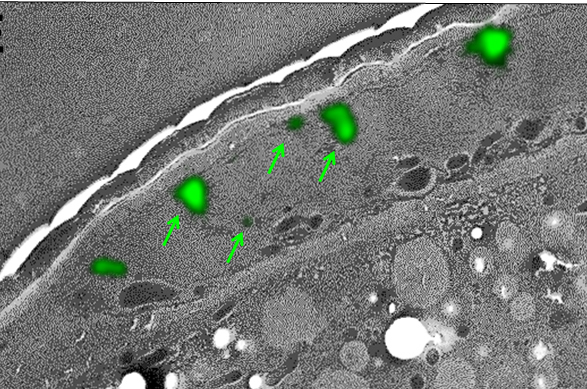
Atg8/LC3 are key actors of selective autophagy through the recognition of the cargoes to be degraded and the formation of the autophagosomes. We discovered that the paternal mitochondria are degraded after fertilization by a selective mitophagy process.
Reticulon dependent ER-phagy mediates adaptation to heat stress in C. elegans
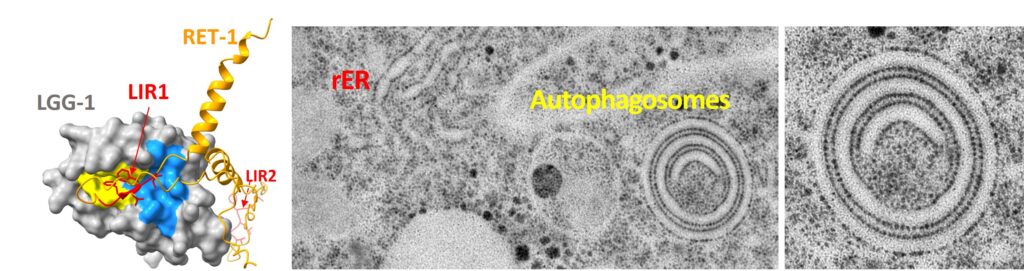
Vincent Scarcelli, Claudia Serot, Alexandre Pouget, Céline Largeau, Audrey Sagot, Kenza El-Hachimi, Denis Dupuy, Emmanuel Culetto, Christophe Lefebvre, Renaud Legouis Reticulon dependent ER-phagy mediates adaptation to heat stress in C. elegans. bioRxiv 2024.07.26.605287
Leboutet R, Chen Y, Legouis R*, Culetto E*. Mitophagy during development and stress in C. elegans. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020 May 23;189:111266.111266. Review
Al Rawi S, Louvet-Vallée S, Djeddi A, Sachse M, Culetto E, Hajjar C, Boyd L, Legouis R.*, Galy V*. Postfertilization autophagy of sperm organelles prevents paternal mitochondrial DNA transmission. Science. 2011 Nov 25;334(6059):1144-7
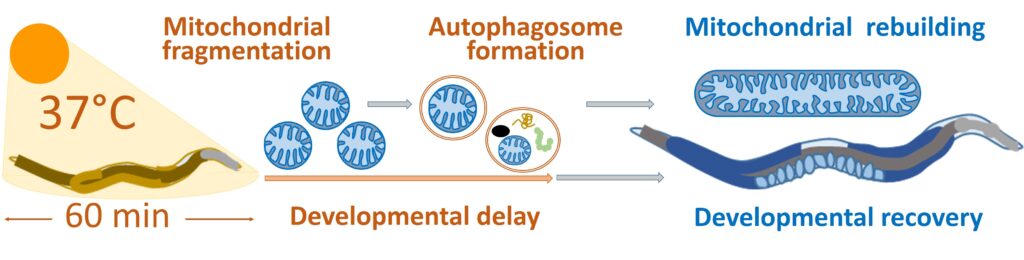
We have developed a new paradigm for studying the adaptation of C. elegans larvae to an acute heat-stress (aHS) that induces a strong developmental defect but no lethality or sterility.
Autophagy facilitates mitochondrial rebuilding and developmental recovery after acute
heat-stress through a DRP-1 dependent process
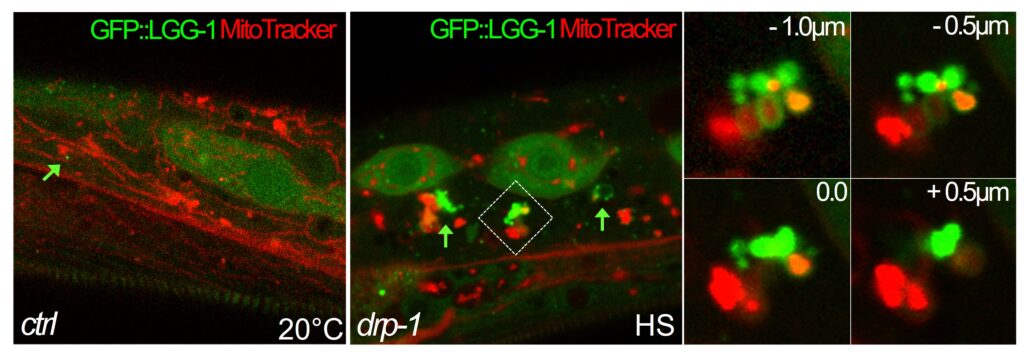
We described how C. elegans copes with aHS, which induces the fragmentation of mitochondria. A DRP-1-dependent autophagy process takes place as part of the worm adaptive mechanism to heat-stress. DRP-1 participates to the coordination between mitochondria fission and autophagosome biogenesis. We also found that mitochondria are a major site for autophagosome biogenesis in the epidermi
Leboutet R, Legouis R. Autophagy facilitates mitochondrial network rebuilding after heat stress in the nematode C. elegans. Med Sci (Paris). 2022;38(6-7):517-519.
Chen Y, Culetto E, Legouis R. The strange case of Drp1 in autophagy: Jekyll and Hyde?. Bioessays. 2022;44(4):e2100271.
Chen Y, Leboutet R, Largeau C, Zentout S, Lefebvre C, Delahodde A, Culetto E, Legouis R. Autophagy facilitates mitochondrial rebuilding after acute heat stress via a DRP-1-dependent process. J Cell Biol. 2021 Apr 5;220(4).
Leboutet R, Chen Y, Legouis R*, Culetto E*. Mitophagy during development and stress in C. elegans. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020 May 23;189:111266.111266. Review
Sulfur starvation-induced autophagy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae involves SAM-dependent signaling and transcription activator Met4
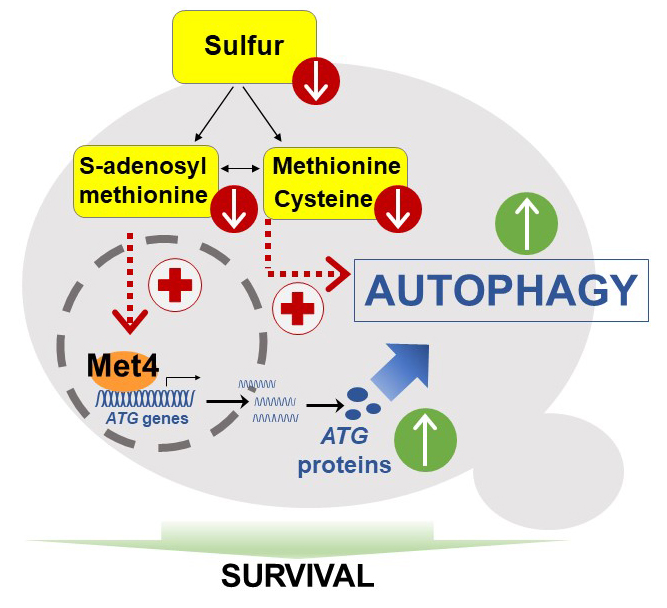
We found that sulfur deprivation leads to rapid and widespread transcriptional induction of autophagy-related (ATG) genes in ways not seen under nitrogen starvation. This distinctive response depends mainly on the transcription activator of sulfur metabolism Met4. Depletion of either cysteine, methionine or SAM induces autophagy flux but only SAM depletion triggers strong transcriptional induction. Thus, we describe a pathway of sulfur starvation induced autophagy depending on Met4 and involving SAM as signaling sulfur metabolite.
New roles of the membrane traffic regulators RabGAP and N-BAR proteins in adapting to nutrients deprivation
in S. cerevisiae
Among adaptations to the deficiency, we focus specifically on autophagy as well as lipid droplets metabolism, and we study specifically the roles of two types of proteins : RabGAP proteins, negative regulators of the Rab GTPases (Fig.A), and N-BAR proteins, able to bend and tubulate membranes (Fig. B).
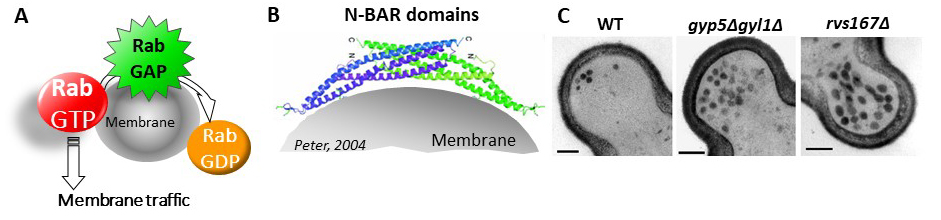
We have previously shown that two RabGAP proteins, Gyp5 and Gyl1, are involved in the control of exocytosis, specifically at the bud tip during the very beginning of bud growth. One of their roles is to recruit the N-BAR protein Rvs167 for exocytosis (Prigent, 2011). Depletion of Gyp5, Gyl1 or Rvs167 leads to a transient accumulation of exocytosis vesicles (Fig. C).
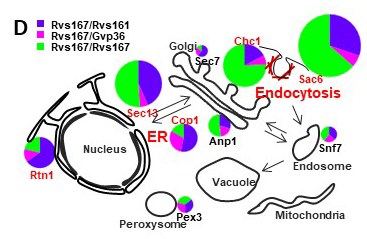
We have shown also that yeast N-BAR domain proteins can form different forms of multimers according to the cellular organelle (FigD; Prigent, 2020). Our recent data show that during nutrients depletion, Gyp5, Gyl1 and Rvs167 redistribute in the cell, interact with new partners and play roles in autophagy, lipid droplets dynamics and cell cycle control.
Prigent, M., Jean-Jacques, H., Naquin, D., Chédin, S., Cuif, M. H., Legouis, R., & Kuras, L.. Sulfur starvation-induced autophagy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae involves SAM-dependent signaling and transcription activator Met4. Nature communications 2024 15(1), 6927.
Prigent M., Chaillot J., Tisserand A., Boy-Marcotte E., Cuif M.H.. Three members of the yeast N-BAR proteins family form heterogeneous lattices in vivo and interact differentially with two RabGAP proteins. Sci. Rep., 2020, vol. 10 1698.
Prigent M., Boy-Marcotte E., Chesneau L., Dupré-Crochet S., Gibson K., Tisserand H., Verbavatz J.M., Cuif M.H. The RabGAP proteins Gyp5p and Gyl1p recruit the BAR domain protein Rvs167p for polarized exocytosis. Traffic, 2011, vol.12, 1084-1097.
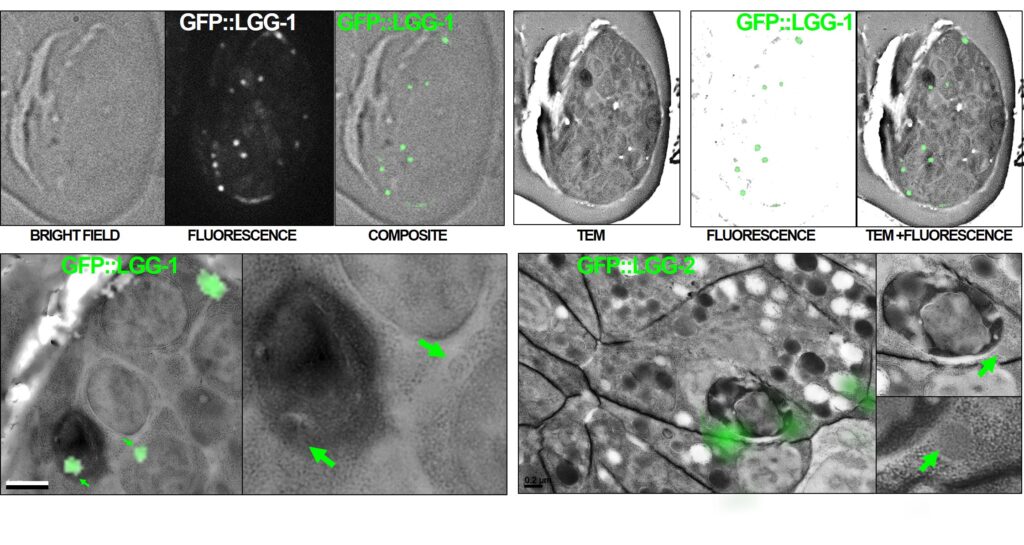
We use a specific fixation protocol which preserves both the GFP fluorescence and the structural integrity of the samples. Thin sections are first analyzed by light microscopy to detect GFP-tagged proteins, then by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to characterize the ultrastructural anatomy of cells. The superimposition of light and electron images allows to determine the subcellular localization of the fluorescent protein.
Exploring selective autophagy events in multiple biologic models using LC3-interacting regions (LIR)-based molecular traps
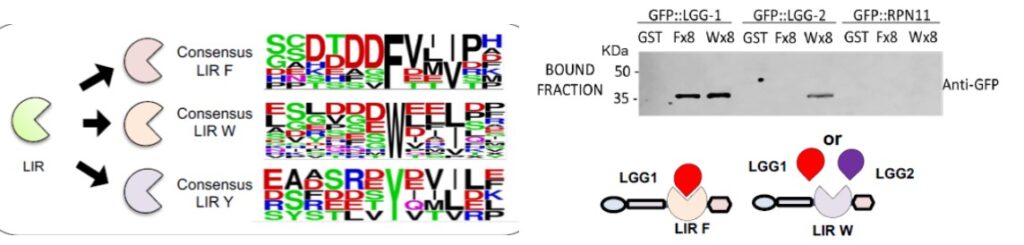
In collaboration with Manuel Rodriguez (LCC, Toulouse), we developped molecular traps based in the tandem disposition of LC3-interacting regions (LIR). The estimated affinity of LC3-traps for distinct recombinant LC3/GABARAP proteins is in the low nanomolar range and allows the capture of these proteins from distinct mammalian cell lines, S. cerevisiae and C. elegans. LC3-traps show preferences for GABARAP/LGG1 or LC3/LGG2 and pull-down substrates targeted to proteaphagy and mitophagy.
In collaborations with a physicist group (Morizet et al. 2019) and a bioinformatician group (Yi et al. 2016) we have also developed new tools for live imaging of C. elegans and analysis of the ubl autophagy interactome, respectively.
Quinet G, Génin P, Belgareh-Touzé N, et al. Analysis of ATG8 Family Members Using LC3-Interacting Regions (LIR)-Based Molecular Traps. Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2602:191-204. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-2859-1_14
Quinet G, Génin P, Ozturk O, et al. Exploring selective autophagy events in multiple biologic models using LC3-interacting regions (LIR)-based molecular traps. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7652. Published 2022 May 10. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-11417-z
Largeau, C., & Legouis, R. Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy to Analyze LC3 Proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans Embryo. Methods in molecular biology 2019, 1880, 281–293.
Morizet,J., Ducourthial, G., Supatto, W., Boutillon,R., Legouis, R., Schanne-Klein,M-C., Stringari, C., & Beaurepaire,E. High-speed polarization-resolved third-harmonic microscopy. Optica 2019 6, 385-388 10.
Le Bars, R., Bianchi, M. W., & Lefebvre, C. Three-Dimensional Surface Rendering of ESCRT Proteins Microscopy Data Using UCSF Chimera Software. Methods in molecular biology 2019 , 1998, 149–161.
Largeau, C., Culetto, E., & Legouis, R.. Subcellular Localization of ESCRT-II in the Nematode C. elegans by Correlative Light Electron Microscopy. Methods in molecular biology 2019, 1998, 49–61.
Chen Y, Scarcelli V, Legouis R. Approaches for Studying Autophagy in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cells. 2017 Aug 30;6(3). Review
Yi Z, Manil-Ségalen M, Sago L, Glatigny A, Redeker V, Legouis R*, Mucchielli-Giorgi MH*. SAFER, an Analysis Method of Quantitative Proteomic Data, Reveals New Interactors of the C. elegans Autophagic Protein LGG-1. J Proteome Res. 2016 May 6;15(5):1515-23.
Zhang H, Chang JT, Guo B, Hansen M, Jia K, Kovács AL, Kumsta C, Lapierre LR, Legouis R, Lin L, Lu Q, Meléndez A, O’Rourke EJ, Sato K, Sato M, Wang X, Wu F. Guidelines for monitoring autophagy in Caenorhabditis elegans. Autophagy. 2015;11(1):9-27.
Jenzer C, Simionato E, Legouis R. Tools and methods to analyze autophagy in C. elegans. Methods. 2015 Mar;75:162-71.